Surgical Sutures Explained: Types & Functions
What Are Surgical Sutures?
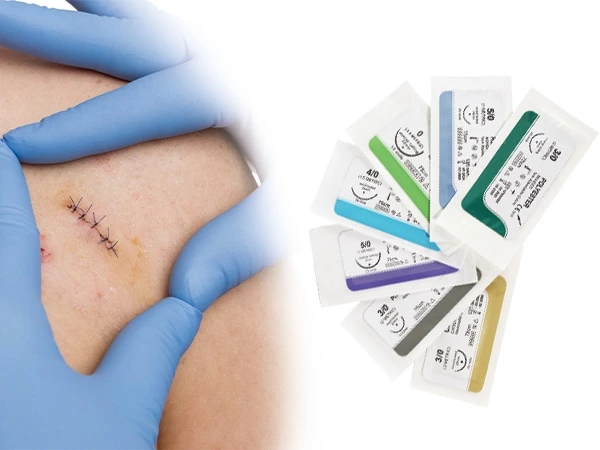
Surgical sutures are sterile medical threads used to close surgical incisions or traumatic wounds. Modern sutures range from traditional silk threads to advanced absorbable polymer materials that dissolve naturally. As critical wound closure devices, they prevent infection while promoting tissue healing processes.
Types of Surgical Sutures
I. Absorbable Sutures: Naturally Dissolving Support
Absorbable sutures are designed to be broken down by the body over time, eliminating the need for removal. These sutures are ideal for internal tissues, soft tissue repairs, and surgeries where natural healing can take over after initial stabilization.
1. Polyglycolic Acid (PGA)
-
Synthetic braided suture with excellent strength and predictable absorption
-
Maintains tensile strength for 2–3 weeks
-
Fully absorbed in 60–90 days
-
Common in gastrointestinal and gynecological procedures
2. Polyglactin 910
-
Smooth handling, minimal tissue reaction
-
Retains 60–70% of strength after 2 weeks
-
Complete absorption within 56–70 days
-
Ideal for soft tissue approximation, ligation, and general surgery
3. Poliglecaprone
-
Monofilament suture with low tissue drag
-
Strength retention: 1–2 weeks
-
Absorption: 90–120 days
-
Preferred for subcuticular closure, plastic surgery, and delicate tissue repairs
4. Polydioxanone (PDS)
-
Long-term absorbable monofilament
-
Retains strength for up to 6 weeks
-
Fully absorbed within 180–210 days
-
Excellent for fascia, tendons, and other tissues requiring prolonged support
5. Catgut (Plain & Chromic)
-
Natural suture made from sheep or cow intestines
-
Easy to handle, good knot security
-
Chromic catgut is treated to slow down absorption
-
Often used in general surgery, gynecology, and veterinary medicine II. Non-Absorbable Sutures: Long-Term Stability
-
Non-absorbable sutures are designed to remain in the body indefinitely or be removed after healing. They are typically used where extended wound support is needed or for external skin closure.
1. Silk
-
Natural multifilament with excellent knotting ability
-
Biodegradable over time but not considered absorbable
-
Elicits more tissue reaction
-
Suitable for ophthalmic, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal procedures
-
2. Nylon (Polyamide)
-
Available in monofilament or braided form
-
3. Polypropylene
-
Inert monofilament with minimal tissue response
-
Ideal for vascular, cardiac, and plastic surgery
-
High strength and flexibility make it suitable for long-term implants
-
4. Polyester
-
Braided synthetic suture coated for smoother handling
-
Exceptional knot security and tensile strength
-
Used in orthopedic, cardiovascular, and soft tissue surgeries
-
High tensile strength, low tissue reactivity
-
Frequently used for skin closure, microsurgery, and ophthalmic surgery
Surgical Sutures Functions
✅ Primary Closure
Aligns wound edges for scar minimization
✅ Hemostasis Control
Applies pressure to bleeding vessels
✅ Tissue Layer Approximation
Multi-layered closure for abdominal surgery or orthopedic procedures
✅ Infection Barrier
Reduces microbial entry with proper suture spacing techniques
✅ Healing Guidance
Absorbable variants support internal healing timelines